Picture a dynamic financial institution where every transaction, investment, and loan is carefully monitored and managed. Behind the scenes, a crucial tool facilitates the seamless operation of these intricate processes: the Entity-Relationship (ER) diagram. In the realm of finance, er diagram finance serve as unsung heroes, offering a clear and structured framework for handling extensive data. This article explores the complexities of er diagram financeer diagram finance finance and highlights their vital role in developing efficient financial management systems.
What is an er diagram finance?
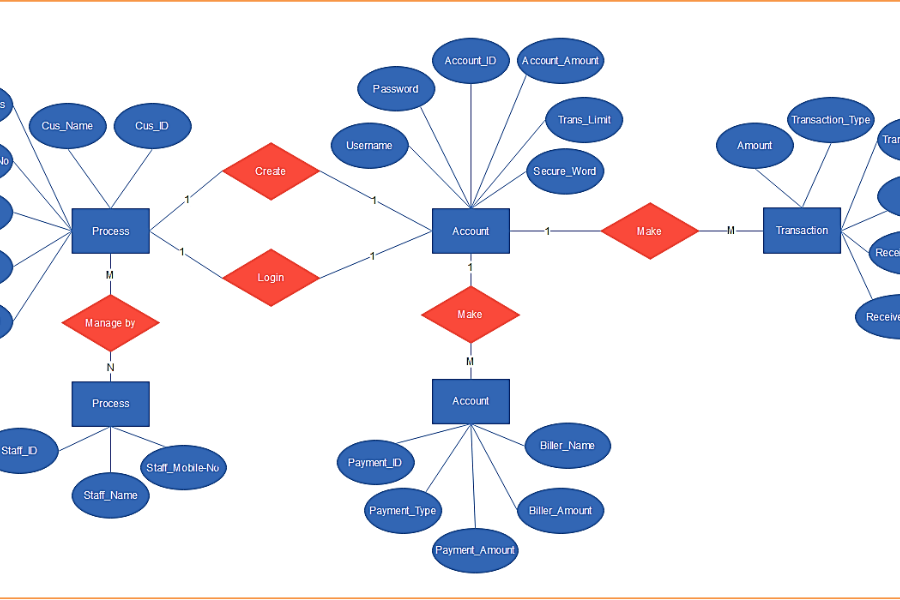
An er diagram finance is a graphical representation that outlines the entities within a system and the relationships that connect them. In the financial sector, these entities may include customers, accounts, transactions, and various financial products. The relationships delineate how these entities interact with one another, forming the foundation of any financial database.
Key Components of er diagram finance
Entities
Entities are the core elements of aner diagram finance. In finance, common entities encompass:
- Customer: Refers to individuals or organizations utilizing financial services.
- Account: Encompasses various account types such as savings, checking, and loans.
- Transaction: Records all financial activities, including deposits, withdrawals, and transfers.
Attributes
Attributes provide further detail about each entity. For instance:
- Customer: Name, address, and contact information.
- Account: Account number, type, and balance.
- Transaction: Transaction ID, date, and amount.
Relationships
Relationships depict how entities are interconnected. In financial systems, typical relationships include:
- Customer-Account: A customer can hold multiple accounts.
- Account-Transaction: An account may have numerous transactions.
Designing an er diagram finance for Financial Systems
Developing an er diagram financefor a financial system involves several key steps:
- Identify Entities: Determine the essential entities relevant to the financial system.
- Define Attributes: Specify the attributes associated with each entity.
- Establish Relationships: Define the interactions between entities.
- Draw the Diagram: Utilize standard notations to visually represent entities, attributes, and relationships.
Benefits of er diagram finance
er diagram financeffer a multitude of advantages in financial management:
- Clarity: They provide a clear and organized framework for complex data.
- Efficiency: Enhances database design, resulting in quicker and more effective data retrieval.
- Scalability: Facilitates easy updates and modifications as financial systems evolve.
Common Challenges and Solutions
Despite their power, er diagram finance can present certain challenges:
- Complexity: Financial systems may be intricate, leading to complicateder diagram finance.
- Maintenance: Keeping the diagram current with system changes requires ongoing effort.
To address these challenges, it’s crucial to:
- Simplify: Break down complex systems into smaller, manageable parts.
- Automate: Use software tools to streamline updates and maintenance.
FAQs
1. What is an er diagram finance?
An er diagram finance(Entity-Relationship diagram) is a visual representation of the entities within a system and the relationships between them. It is used to design and model the data structure of a database.
2. What are the main components of an er diagram finance?
The main components of aner diagram finance include entities (such as customers, accounts, and transactions), attributes (details about each entity), and relationships (how entities interact with each other).
3. Why are er diagram finance important in finance?
er diagram finance are crucial in finance because they provide a clear and structured framework for managing complex data. They enhance database design, improve data retrieval efficiency, and facilitate scalability as financial systems evolve.
4. What are some common entities found in a financial er diagram finance?
Common entities in a financial er diagram finance include customers, accounts, transactions, and financial products.
5. How do you create an er diagram finance for a financial system?
To create an er diagram finance, you should identify the essential entities, define their attributes, establish relationships, and then draw the diagram using standard notations.
6. What challenges can arise when using er diagram finances in finance?
Challenges may include complexity due to intricate systems and the need for ongoing maintenance to keep the diagram updated with system changes.
7. How can these challenges be addressed?
To address these challenges, consider simplifying complex systems into manageable parts and using software tools to automate updates and maintenance.
Conclusion
In the financial sector, er diagram finance play a pivotal role in establishing efficient management systems. By providing a clear and structured overview of the data architecture, they enable financial institutions to effectively monitor and manage transactions, accounts, and customer information. As the financial landscape continues to evolve, the significance of er diagram finance will only grow, reinforcing their position as an essential tool for data organization and system optimization in modern financial management.



Leave a Reply